
Security News
Deno 2.2 Improves Dependency Management and Expands Node.js Compatibility
Deno 2.2 enhances Node.js compatibility, improves dependency management, adds OpenTelemetry support, and expands linting and task automation for developers.
cspell is a spell checker for code that helps developers identify and correct spelling errors in their codebase, comments, strings, and documentation. It is highly configurable and can be integrated into various development workflows.
Basic Spell Checking
This command runs cspell to check for spelling errors in all TypeScript files within the 'src' directory and its subdirectories.
npx cspell 'src/**/*.ts'Custom Dictionaries
You can add custom dictionaries to cspell by specifying them in the configuration file. This allows you to include domain-specific terms that are not in the default dictionary.
{
"dictionaries": ["custom-words"]
}Ignoring Files and Patterns
cspell allows you to ignore specific files or patterns by adding them to the 'ignorePaths' array in the configuration file. This is useful for excluding generated files or dependencies.
{
"ignorePaths": ["node_modules/**", "dist/**"]
}Configurable Language Settings
You can configure the language and locale settings in cspell to match the language used in your codebase. This ensures that the spell checker uses the correct dictionary and rules.
{
"language": "en",
"local": "en-US"
}Integration with Code Editors
cspell can be integrated with popular code editors like VSCode. By enabling the cspell extension, you can get real-time spell checking as you write code.
/* Example for VSCode */
{
"cSpell.enabled": true
}eslint-plugin-spellcheck is an ESLint plugin that checks for spelling errors in comments and string literals. It is less comprehensive than cspell but integrates directly with ESLint, making it a good choice for projects already using ESLint.
spellchecker is a simple spell checking library that can be used in Node.js applications. It provides basic spell checking functionality but lacks the extensive configuration options and integrations that cspell offers.
hunspell-spellchecker is a Node.js wrapper for the Hunspell spell checker. It provides powerful spell checking capabilities but requires more setup and configuration compared to cspell.
A Spell Checker for Code!
cspell is a command line tool and library for spell checking code.
cspell was initially built as the spell checking service for the spell checker extension for Visual Studio Code.
Available as part of the Tidelift Subscription.
The maintainers of cspell and thousands of other packages are working with Tidelift to deliver commercial support and maintenance for the open source packages you use to build your applications. Save time, reduce risk, and improve code health, while paying the maintainers of the exact packages you use. Learn more.
npm install -g cspell
There is a docker image at Packages for cspell.
cspell commands below can be run by replacing
cspell
with:
docker run -it -v $PWD:/workdir ghcr.io/streetsidesoftware/cspell:latest
Example:
docker run -it -v $PWD:/workdir ghcr.io/streetsidesoftware/cspell:latest lint --help
Example: recursively spell check all JavaScript files in src
JavaScript files
cspell "src/**/*.js"
# or
cspell lint "src/**/*.js"
Check everything
cspell "**"
Git: Check Only Changed Files
git diff --name-only | npx cspell --file-list stdin
lint -- Spell CheckingThe lint command is used for spell checking files.
cspell lint --help
Usage: cspell lint [options] [globs...] [file://<path> ...] [stdin[://<path>]]
Patterns:
- [globs...] Glob Patterns
- [stdin] Read from "stdin" assume text file.
- [stdin://<path>] Read from "stdin", use <path> for file type and config.
- [file://<path>] Check the file at <path>
Examples:
cspell . Recursively check all files.
cspell lint . The same as "cspell ."
cspell "*.js" Check all .js files in the current directory
cspell "**/*.js" Check all .js files recursively
cspell "src/**/*.js" Only check .js under src
cspell "**/*.txt" "**/*.js" Check both .js and .txt files.
cspell "**/*.{txt,js,md}" Check .txt, .js, and .md files.
cat LICENSE | cspell stdin Check stdin
cspell stdin://docs/doc.md Check stdin as if it was "./docs/doc.md"
Check spelling
Options:
-c, --config <cspell.json> Configuration file to use. By default cspell
looks for cspell.json in the current directory.
-v, --verbose Display more information about the files being
checked and the configuration.
--locale <locale> Set language locales. i.e. "en,fr" for English
and French, or "en-GB" for British English.
--language-id <file-type> Force programming language for unknown
extensions. i.e. "php" or "scala"
--words-only Only output the words not found in the
dictionaries.
-u, --unique Only output the first instance of a word not
found in the dictionaries.
-e, --exclude <glob> Exclude files matching the glob pattern. This
option can be used multiple times to add multiple
globs.
--file-list <path or stdin> Specify a list of files to be spell checked. The
list is filtered against the glob file patterns.
Note: the format is 1 file path per line.
--file [file...] Specify files to spell check. They are filtered
by the [globs...].
--no-issues Do not show the spelling errors.
--no-progress Turn off progress messages
--no-summary Turn off summary message in console.
-s, --silent Silent mode, suppress error messages.
--no-exit-code Do not return an exit code if issues are found.
--quiet Only show spelling issues or errors.
--fail-fast Exit after first file with an issue or error.
-r, --root <root folder> Root directory, defaults to current directory.
--no-relative Issues are displayed with absolute path instead
of relative to the root.
--show-context Show the surrounding text around an issue.
--show-suggestions Show spelling suggestions.
--no-show-suggestions Do not show spelling suggestions or fixes.
--no-must-find-files Do not error if no files are found.
--cache Use cache to only check changed files.
--no-cache Do not use cache.
--cache-reset Reset the cache file.
--cache-strategy <strategy> Strategy to use for detecting changed files.
(choices: "content", "metadata", default:
"content")
--cache-location <path> Path to the cache file or directory. (default:
".cspellcache")
--dot Include files and directories starting with `.`
(period) when matching globs.
--gitignore Ignore files matching glob patterns found in
.gitignore files.
--no-gitignore Do NOT use .gitignore files.
--gitignore-root <path> Prevent searching for .gitignore files past root.
--validate-directives Validate in-document CSpell directives.
--color Force color.
--no-color Turn off color.
--no-default-configuration Do not load the default configuration and
dictionaries.
--debug Output information useful for debugging
cspell.json files.
--reporter <module|path> Specify one or more reporters to use.
--issue-template [template] Use a custom issue template. See --help
--issue-template for details.
-h, --help display help for command
More Examples:
cspell "**/*.js" --reporter @cspell/cspell-json-reporter
This will spell check all ".js" files recursively and use
"@cspell/cspell-json-reporter".
cspell . --reporter default
This will force the default reporter to be used overriding
any reporters defined in the configuration.
cspell . --reporter ./<path>/reporter.cjs
Use a custom reporter. See API for details.
cspell "*.md" --exclude CHANGELOG.md --files README.md CHANGELOG.md
Spell check only check "README.md" but NOT "CHANGELOG.md".
cspell "/*.md" --no-must-find-files --files $FILES
Only spell check the "/*.md" files in $FILES,
where $FILES is a shell variable that contains the list of files.
References:
https://cspell.org
https://github.com/streetsidesoftware/cspell
check - Quick Visual CheckDo a quick visual check of a file. This is a great way to see which text is included in the check.
cspell check <filename>
It will produce something like this:
lessTo get color in less, use --color and less -r
cspell check <filename> --color | less -r
trace - See which dictionaries contain a wordTrace shows a the list of known dictionaries and a * next to the ones that contain the word.
A ! will appear next to the ones where the word is forbidden.
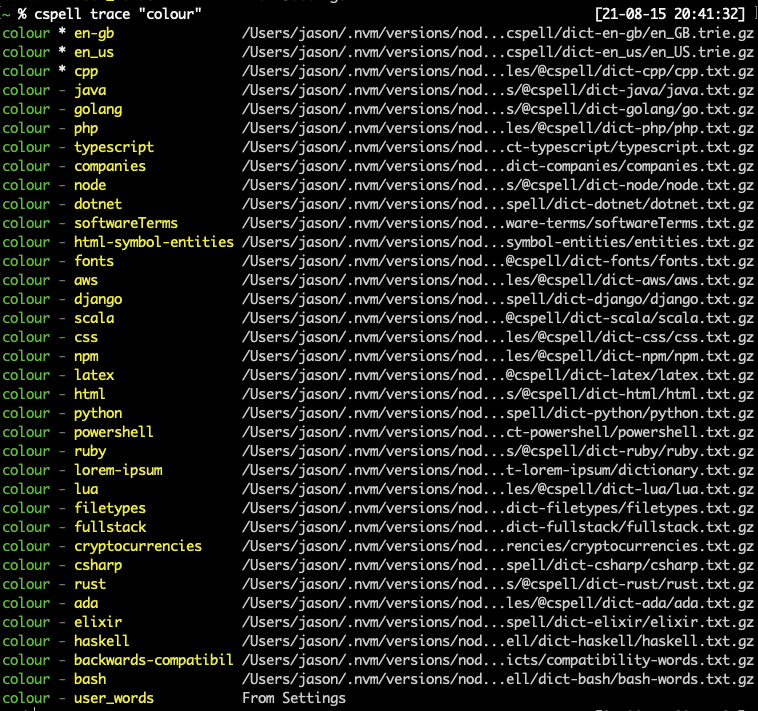
cspell trace --helpUsage: cspell trace [options] [words...]
Trace words -- Search for words in the configuration and dictionaries.
Options:
-c, --config <cspell.json> Configuration file to use. By default cspell
looks for cspell.json in the current directory.
--locale <locale> Set language locales. i.e. "en,fr" for English and
French, or "en-GB" for British English.
--language-id <language> Use programming language. i.e. "php" or "scala".
--allow-compound-words Turn on allowCompoundWords
--no-allow-compound-words Turn off allowCompoundWords
--ignore-case Ignore case and accents when searching for words.
--no-ignore-case Do not ignore case and accents when searching for
words.
--dictionary-path <format> Configure how to display the dictionary path.
(choices: "hide", "short", "long", "full",
default: Display most of the path.)
--stdin Read words from stdin.
--all Show all dictionaries.
--only-found Show only dictionaries that have the words.
--color Force color.
--no-color Turn off color.
--no-default-configuration Do not load the default configuration and
dictionaries.
-h, --help display help for command
Mega-Linter aggregates 70 linters ready to use out of the box, including cspell
.cspell.json file with new unknown wordsSetup
Quick setup following installation guide in Mega-Linter documentation
Setup
npm install -SD cspell
.git/hooks/pre-commit
#!/bin/sh
exec git diff --cached --name-only | npx cspell --no-summary --no-progress --no-must-find-files --file-list stdin
CSpell needs Node 18 and above.
The concept is simple, split camelCase and snake_case words before checking them against a list of known words.
camelCase -> camel caseHTMLInput -> html inputsrcCode -> src codesnake_case_words -> snake case wordscamel2snake -> camel snake -- (the 2 is ignored)function parseJson(text: string) -> function parse json text string\n, \t are removed if the word does not match:
\narrow -> narrow - because narrow is a word\ncode -> code - because ncode is not a word.\network -> network - but it might be hiding a spelling error, if \n was an escape character.english which should be English.It is possible to add spell check settings into your source code. This is to help with file specific issues that may not be applicable to the entire project.
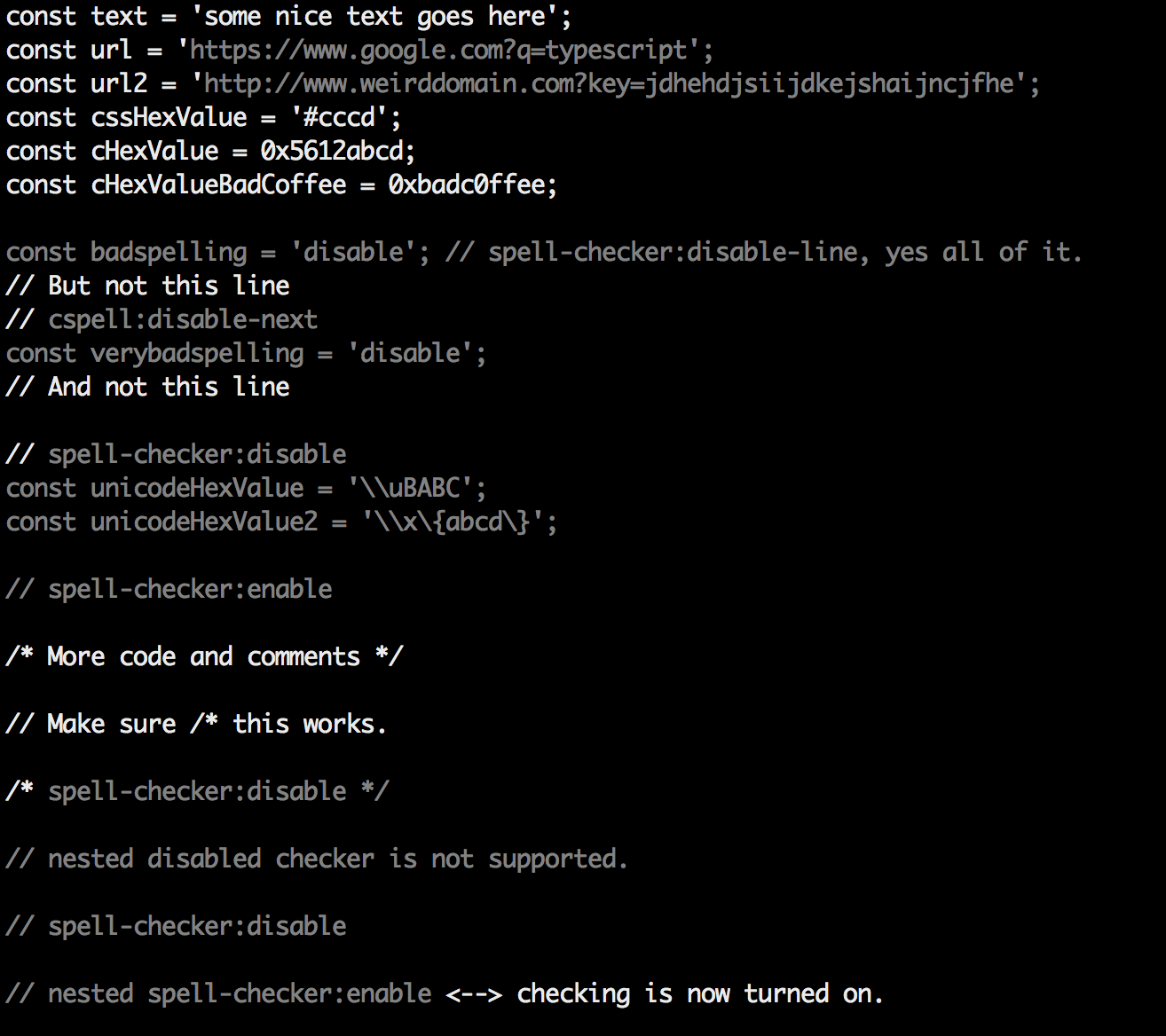
All settings are prefixed with cspell: or spell-checker:.
disable -- turn off the spell checker for a section of code.enable -- turn the spell checker back on after it has been turned off.ignore -- specify a list of words to be ignored.words -- specify a list of words to be considered correct and will appear in the suggestions list.ignoreRegExp -- Any text matching the regular expression will NOT be checked for spelling.includeRegExp -- Only text matching the collection of includeRegExp will be checked.enableCompoundWords / disableCompoundWords -- Allow / disallow words like: "stringlength".dictionaries -- specify a list of the names of the dictionaries to use.It is possible to disable / enable the spell checker by adding comments to your code.
/* cspell:disable *//* spell-checker: disable *//* spellchecker: disable */// cspell:disable-line -- disables checking for the current line./* cspell:disable-next-line */ -- disables checking till the end of the next line./* cspell:enable *//* spell-checker: enable *//* spellchecker: enable */// cspell:disable
const wackyWord = ['zaallano', 'wooorrdd', 'zzooommmmmmmm'];
/* cspell:enable */
const words = ['zaallano', 'wooorrdd', 'zzooommmmmmmm']; // cspell:disable-line disables this entire line
// To disable the next line, use cspell:disable-next-line
const moreWords = ['ieeees', 'beees', 'treeees'];
// Nesting disable / enable is not Supported
// spell-checker:disable
// It is now disabled.
var liep = 1;
/* cspell:disable */
// It is still disabled
// cspell:enable
// It is now enabled
const str = 'goededag'; // <- will be flagged as an error.
// spell-checker:enable <- doesn't do anything
// cSPELL:DISABLE <-- also works.
// if there isn't an enable, spelling is disabled till the end of the file.
const str = 'goedemorgen'; // <- will NOT be flagged as an error.
Ignore allows you the specify a list of words you want to ignore within the document.
// cspell:ignore zaallano, wooorrdd
// cspell:ignore zzooommmmmmmm
const wackyWord = ['zaallano', 'wooorrdd', 'zzooommmmmmmm'];
Note: words defined with ignore will be ignored for the entire file.
The words list allows you to add words that will be considered correct and will be used as suggestions.
// cspell:words woorxs sweeetbeat
const companyName = 'woorxs sweeetbeat';
Note: words defined with words will be used for the entire file.
In some programming language it is common to glue words together.
// cspell:enableCompoundWords
char * errormessage; // Is ok with cspell:enableCompoundWords
int errornumber; // Is also ok.
Note: Compound word checking cannot be turned on / off in the same file. The last setting in the file determines the value for the entire file.
By default, the entire document is checked for spelling.
cspell:disable/cspell:enable above allows you to block off sections of the document.
ignoreRegExp and includeRegExp give you the ability to ignore or include patterns of text.
By default the flags gim are added if no flags are given.
The spell checker works in the following way:
includeRegExpignoreRegExp// cspell:ignoreRegExp 0x[0-9a-f]+ -- will ignore c style hex numbers
// cspell:ignoreRegExp /0x[0-9A-F]+/g -- will ignore upper case c style hex numbers.
// cspell:ignoreRegExp g{5} h{5} -- will only match ggggg, but not hhhhh or 'ggggg hhhhh'
// cspell:ignoreRegExp g{5}|h{5} -- will match both ggggg and hhhhh
// cspell:ignoreRegExp /g{5} h{5}/ -- will match 'ggggg hhhhh'
/* cspell:ignoreRegExp /n{5}/ -- will NOT work as expected because of the ending comment -> */
/*
cspell:ignoreRegExp /q{5}/ -- will match qqqqq just fine but NOT QQQQQ
*/
// cspell:ignoreRegExp /[^\s]{40,}/ -- will ignore long strings with no spaces.
// cspell:ignoreRegExp Email -- this will ignore email like patterns -- see Predefined RegExp expressions
var encodedImage = 'HR+cPzr7XGAOJNurPL0G8I2kU0UhKcqFssoKvFTR7z0T3VJfK37vS025uKroHfJ9nA6WWbHZ/ASn...';
var email1 = 'emailaddress@myfancynewcompany.com';
var email2 = '<emailaddress@myfancynewcompany.com>';
Note: ignoreRegExp and includeRegExp are applied to the entire file. They do not start and stop.
In general you should not need to use includeRegExp. But if you are mixing languages then it could come in helpful.
# cspell:includeRegExp #.*
# cspell:includeRegExp ("""|''')[^\1]*\1
# only comments and block strings will be checked for spelling.
def sum_it(self, seq):
"""This is checked for spelling"""
variabele = 0
alinea = 'this is not checked'
for num in seq:
# The local state of 'value' will be retained between iterations
variabele += num
yield variabele
The dictionaries list allows you to specify dictionaries to use for the file.
// cspell:dictionaries lorem-ipsum
const companyName = 'Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet';
Note: dictionaries specified with dictionaries will be used for the entire file.
Urls1 -- Matches urlsHexValues -- Matches common hex format like #aaa, 0xfeef, \u0134Base641 -- matches base64 blocks of text longer than 40 characters.Email -- matches most email addresses.Everything1 -- By default we match an entire document and remove the excludes.string -- This matches common string formats like '...', "...", and `...`CStyleComment -- These are C Style comments /* */ and //PhpHereDoc -- This matches PHPHereDoc strings.1. These patterns are part of the default include/exclude list for every file.
cspell's behavior can be controlled through a config file. By default it looks for any of the following files:
.cspell.jsoncspell.json.cSpell.jsoncSpell.jsoncspell.config.jscspell.config.cjscspell.config.jsoncspell.config.yamlcspell.config.ymlcspell.yamlcspell.ymlOr you can specify a path to a config file with the --config <path> argument on the command line.
cspell.jsoncspell.json file// cSpell Settings
{
// Version of the setting file. Always 0.2
"version": "0.2",
// language - current active spelling language
"language": "en",
// words - list of words to be always considered correct
"words": [
"mkdirp",
"tsmerge",
"githubusercontent",
"streetsidesoftware",
"vsmarketplacebadge",
"visualstudio"
],
// flagWords - list of words to be always considered incorrect
// This is useful for offensive words and common spelling errors.
// For example "hte" should be "the"
"flagWords": [
"hte"
]
}
version - currently always 0.2 - controls how the settings in the configuration file behave.
language - this specifies the language locale to use in choosing the general dictionary.
For example: "language": "en-GB" tells cspell to use British English instead of US English.
words - a list of words to be considered correct.
flagWords - a list of words to be always considered incorrect
ignoreWords - a list of words to be ignored (even if they are in the flagWords).
ignorePaths - a list of globs to specify which files are to be ignored.
Example
"ignorePaths": ["node_modules/**"]
will cause cspell to ignore anything in the node_modules directory.
maxNumberOfProblems - defaults to 100 per file.
minWordLength - defaults to 4 - the minimum length of a word before it is checked.
allowCompoundWords - defaults to false; set to true to allow compound words by default.
dictionaries - list of the names of the dictionaries to use. See Dictionaries below.
dictionaryDefinitions - this list defines any custom dictionaries to use. This is how you can include other languages like Spanish.
Example
"language": "en",
// Dictionaries "spanish", "ruby", and "corp-term" will always be checked.
// Including "spanish" in the list of dictionaries means both Spanish and English
// words will be considered correct.
"dictionaries": ["spanish", "ruby", "corp-terms", "fonts"],
// Define each dictionary. Relative paths are relative to the config file.
"dictionaryDefinitions": [
{ "name": "spanish", "path": "./spanish-words.txt"},
{ "name": "ruby", "path": "./ruby.txt"},
{ "name": "company-terms", "path": "./corp-terms.txt"}
],
ignoreRegExpList - list of patterns to be ignored
includeRegExpList - (Advanced) limits the text checked to be only that matching the expressions in the list.
patterns - this allows you to define named patterns to be used with
ignoreRegExpList and includeRegExpList.
languageSettings - this allow for per programming language configuration settings. See LanguageSettings
The spell checker includes a set of default dictionaries.
cspell.json file. // Replace various tick marks with a single '
"repMap": [["'|`|’", "'"]]
// Define each dictionary. Relative paths are relative to the config file.
"dictionaryDefinitions": [
{ "name": "spanish", "path": "./spanish-words.txt"},
{ "name": "ruby", "path": "./ruby.txt"},
{ "name": "company-terms", "path": "./corp-terms.txt"}
],
It is possible to prevent a dictionary from being loaded. This is useful if you want to use your own dictionary or just turn off an existing dictionary.
"dictionaries": ["!cpp"],
"overrides": [
{
"filename": "legacy/**/*.cpp",
"dictionaries": ["!!cpp"], // add it back for *.cpp files under the legacy folder
},
]
The number of !s is important.
!cpp remove cpp dictionary!!cpp add it back!!!cpp remove it again.The Language Settings allow configuration to be based upon the programming language and/or the locale.
There are two selector fields locale and languageId.
languageId defines which programming languages to match against.
A value of "python,javascript" will match against python and javascript files. To match against ALL programming languages,
use "*".locale defines which spoken languages to match against. A value of "en-GB,nl" will match against British English or Dutch.
A value of "*" will match all spoken languages.cspell.json file can be define or redefine within the languageSettings. "languageSettings": [
{
// VSCode languageId. i.e. typescript, java, go, cpp, javascript, markdown, latex
// * will match against any file type.
"languageId": "c,cpp",
// Language locale. i.e. en-US, de-AT, or ru. * will match all locales.
// Multiple locales can be specified like: "en, en-US" to match both English and English US.
"locale": "*",
// To exclude patterns, add them to "ignoreRegExpList"
"ignoreRegExpList": [
"/#include.*/"
],
// List of dictionaries to enable by name in `dictionaryDefinitions`
"dictionaries": ["cpp"],
// Dictionary definitions can also be supplied here. They are only used iff "languageId" and "locale" match.
"dictionaryDefinitions": []
}
]
Overrides are useful for forcing configuration on a per file basis.
Example:
"overrides": [
// Force `*.hrr` and `*.crr` files to be treated as `cpp` files:
{
"filename": "**/{*.hrr,*.crr}",
"languageId": "cpp"
},
// Force `*.txt` to use the Dutch dictionary (Dutch dictionary needs to be installed separately):
{
"language": "nl",
"filename": "**/dutch/**/*.txt"
}
]
Brought to you by Street Side Software
Street Side Software
FAQs
A Spelling Checker for Code!
The npm package cspell receives a total of 437,690 weekly downloads. As such, cspell popularity was classified as popular.
We found that cspell demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Deno 2.2 enhances Node.js compatibility, improves dependency management, adds OpenTelemetry support, and expands linting and task automation for developers.

Security News
React's CRA deprecation announcement sparked community criticism over framework recommendations, leading to quick updates acknowledging build tools like Vite as valid alternatives.

Security News
Ransomware payment rates hit an all-time low in 2024 as law enforcement crackdowns, stronger defenses, and shifting policies make attacks riskier and less profitable.